Clear Radar Upgrade
(CRU)
Technical Requirements Document
(TRD)
1.0 SCOPE 1 1.1 Identification 1 1.2 System Description 1 1.3 Document Overview 12. APPLICABLE DOCUMENTS 33. SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS 5 3.1 Definition 5 4.0 QUALITY ASSURANCE PROVISIONS 7 4.1 Verification Concept 7 4.2 Verification Cross Reference Index 7 4.2.1 Inspection 7 4.2.2 Analysis 7 4.2.3 Demonstration 7 4.2.4 Test 7
List of Figures
1.0 SCOPE1.0 SCOPE
1.1 Identification1.1 Identification. This requirements document establishes the set of performance and functional requirements for a ground based, solid state phased array radar to be located at Clear AS, AK. The primary mission area of CRU is the Office of the Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition (OUSD(A)) Mission Area No. 332, Strategic Surveillance and Warning. The secondary mission areas are OUSD(A) No. 120, Strategic Defense, and OUSD(A) No.123, Space Defense.
1.2 System Description1.2 System Description. The BMEWS radars currently operational at Clear AS provide tactical warning and attack assessment of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBM) and submarine launched ballistic missiles (SLBM) launched from Eurasia and the Arctic Ocean against North America. These radars also perform a secondary mission of space surveillance.
The Clear Radar Upgrade (CRU) program will replace the existing mechanical radars with an AN/FPS-123 Phased Array Warning System (PAVE PAWS) radar at Clear AS, AK. The radar will include government provided prime mission equipment (PME) from the sites at Robins, GA and Eldorado, TX, which will be integrated into a newly constructed structure at Clear AS. CRU addresses Air Force Space Command (AFSPC) requirements for reduced operations and maintenance (O&M) costs, improved quality and accuracy of missile warning and space surveillance data, and elimination of coverage gaps. AFSPC has designated January 2001 as the required initial operational capability (IOC) date.
1.3 Document Overview1.3 Document Overview. Sections 2 through 4 of this document identify the requirements for operation and verification of the CRU solid state phased array radar.
2. APPLICABLE DOCUMENTS2. APPLICABLE DOCUMENTS
The following documents of the exact issue shown form a part of this requirements document to the extent specified. In the event of conflict between the documents referenced herein and the contents of this requirements document, the contents of this requirements document shall be considered a superseding requirement.
ESD/SCT-0001A System Performance
CODE IDENT: 50464 Specification For Phased
13 JULY 1987 Array Warning System,
Including Specification PAVE PAWS AN/FPS-123 (V)1,
Change Notice (SCN) (V)2, (V)3, (V)4
1-002, 15 September 1995
AF Form 1067, 12 Nov 1996 Modification Proposal, Clear Radar
(Draft) Upgrade
Appendix A, 24 March 1997 Requirements Correlation Matrix
(Draft) (S-RELCAN)
Technical Requirements Document CENPA Facilities Requirements
(Draft) (Placeholder)
3. SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS3. SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
3.1 Definition3.1 Definition. The CRU will support the Air Force Space Command (AFSPC) missions to provide warning and assessment of Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) or Sea Launched Ballistic Missile (SLBM) attacks against North America and space surveillance and Space Object Identification.
3.2 Performance Characteristics. The technical performance requirements for the CRU are contained in the reference ESD/SCT-0001A and its annexes except as modified by this Technical Requirements Document (TRD) and its companion Facilities TRD (Need the correct title for this document). 3.2 Performance Characteristics
3.2.1 Minimum System Capacities3.2.1 Minimum System Capacities. The minimum acceptable performance and system capacities are contained in the referenced Modification Request, AF Form 1067, and Annex A, Requirements Correlation Matrix.
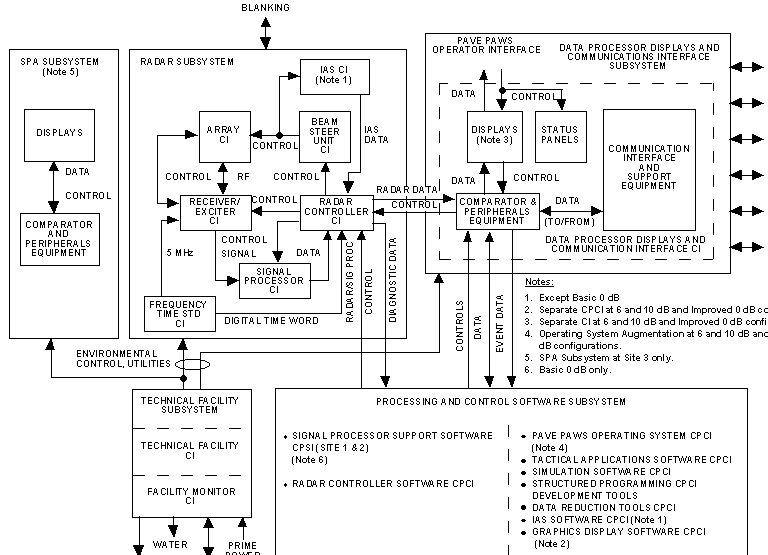
3.3 Functional Characteristics. The CRU system functions are organized into four subsystems: Radar Subsystem; Data Processor, Display and Communications Interface Subsystem; Processor and Control Software Subsystem; and Technical Facility Subsystem. Figure 3-1 represents the functional connectivity among the four subsystems.
4.0 QUALITY ASSURANCE PROVISIONS4.0 QUALITY ASSURANCE PROVISIONS
4.1 Verification Concept4.1 Verification Concept. Contractor verification of CRU requirements shall be in accordance with the CRU Performance Work Statement (PWS). The requirements to be verified during each type of activity (described in the PWS) are identified in the attached verification cross reference index (VCRI).
4.2 Verification Cross Reference Index4.2 Verification Cross Reference Index. Table 1, the VCRI, correlates the requirements of section 3 with the verification requirements of section 4. The type of verification and method of verification for each requirement are provided. Methods of verification (inspection, analysis, demonstration, and test) are defined herein.
4.2.1 Inspection4.2.1 Inspection. Inspection is defined as a visual method of verification that determines compliance with required characteristics without the use of special laboratory equipment, procedures, items or services. Inspection is used to verify construction features, document and drawing compliance, workmanship and physical condition. It involves “looking at” an item or component, or reviewing descriptive documentation , and comparing the appropriate characteristic with a predetermined standard. This method may require moving, turning or partially disassembling hardware to gain visual access, but does not require operation of the item.
4.2.2 Analysis4.2.2 Analysis. Analysis is defined as a method of verification wherein the item or component design is studied to determine if it meets specified requirements. Analysis includes the technical evaluation of drawings, software listings, equations, charts, graphs, diagrams, or representative data.
4.2.3 Demonstration4.2.3 Demonstration. Demonstration is defined as a method of verification denoting the qualitative determination of properties by observation. Demonstration is limited to a readily observable functional operation to determine compliance with requirements. Demonstration may use special test equipment and simulation techniques to create the necessary input environment. Demonstration is primarily used for activities where data gathering is not appropriate such as display verification. Demonstrations are used to indicate pass/fail conditions and to verify characteristics such as proper system response as a result of a specified input command, operational performance, human engineering features, service and access features.
4.2.4 Test4.2.4 Test. Test is defined as a method of verification wherein system performance is measured during or after the controlled application of real or simulated functional and/or environmental stimuli. Measurements of quantitative performance are often taken a sufficient number of times to provide a statistical level of confidence in the final result. System performance measurements may require the use of laboratory equipment, special test equipment, recorders, procedures, items and/or services. Test performance is the means of creating data for detailed analysis. The analysis of data derived from test is an integral part of the activity and may involve automated data reduction to produce the necessary results.

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11